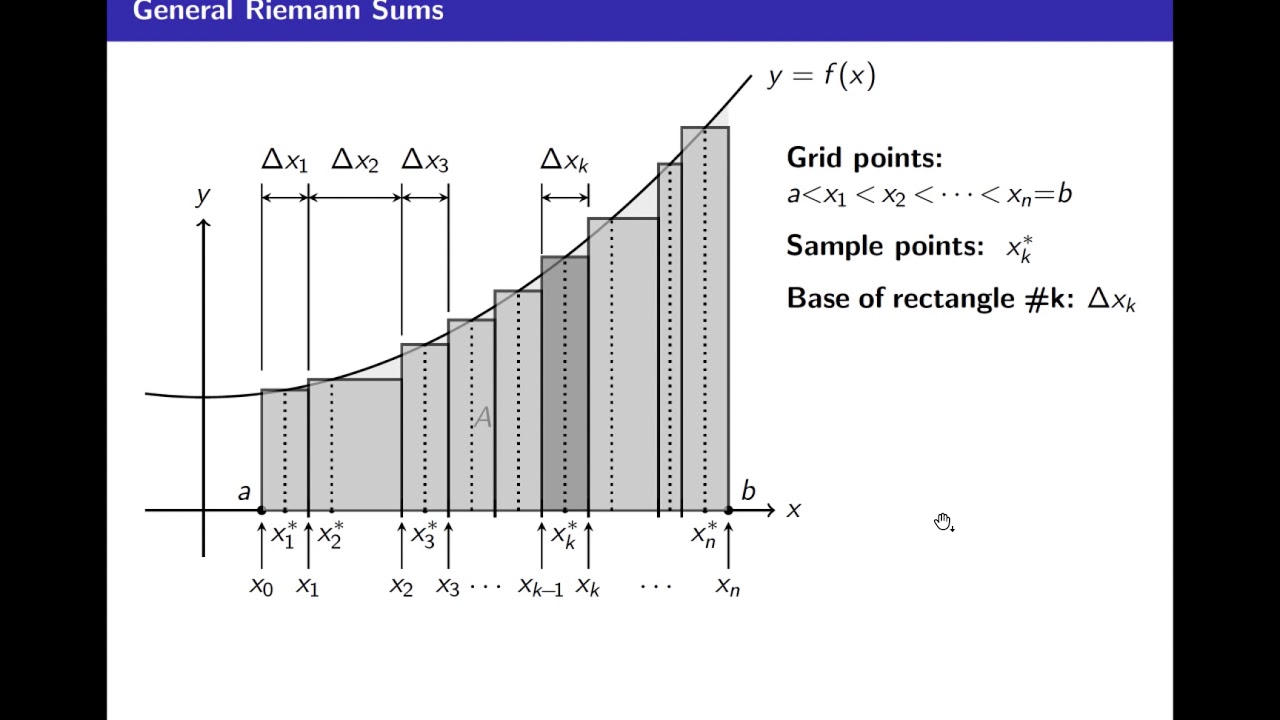
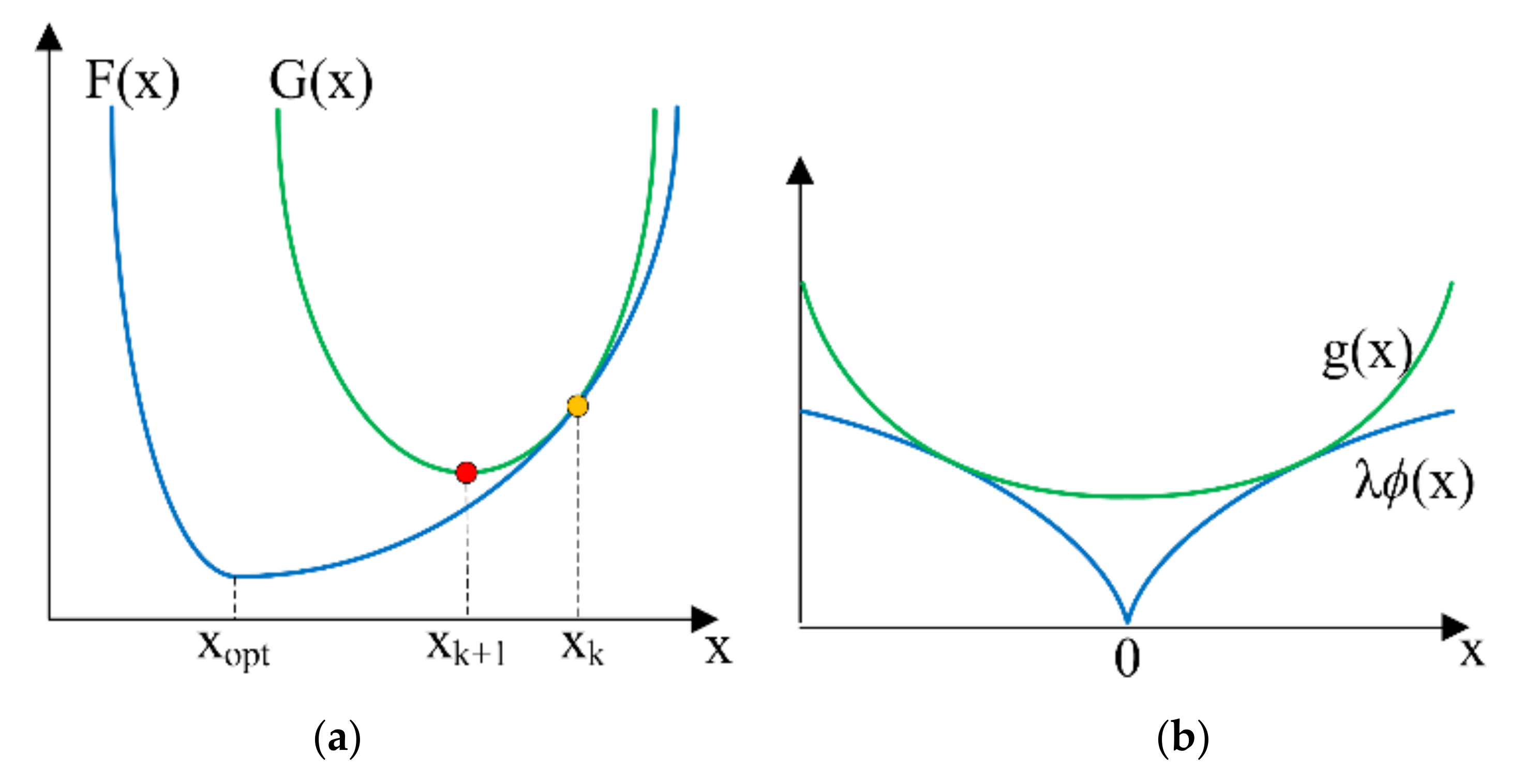
Thus, the xaxis is a horizontal asymptote The equation d d x e x = e x {\displaystyle {\tfrac {d}{dx}}e^{x}=e^{x}} means that the slope of the tangent to the graph at each point is equal to its y coordinate at that pointGiven an equation of the form f (x) = b x c d f (x) = b x c d for x, x, use a graphing calculator to approximate the solution Press Y= Enter the given exponential equation in the line headed "Y 1 =" Enter the given value for f (x) f (x) in the line headed "Y 2 =" Press WINDOW Adjust the yaxis so that it includes the value entered for "Y 2 ="The period is the distance (or time) that it takes for the sine or cosine curve to begin repeating again Graph Interactive Period of a Sine Curve Here's an applet that you can use to explore the concept of period and frequency of a
2
F x b x graph
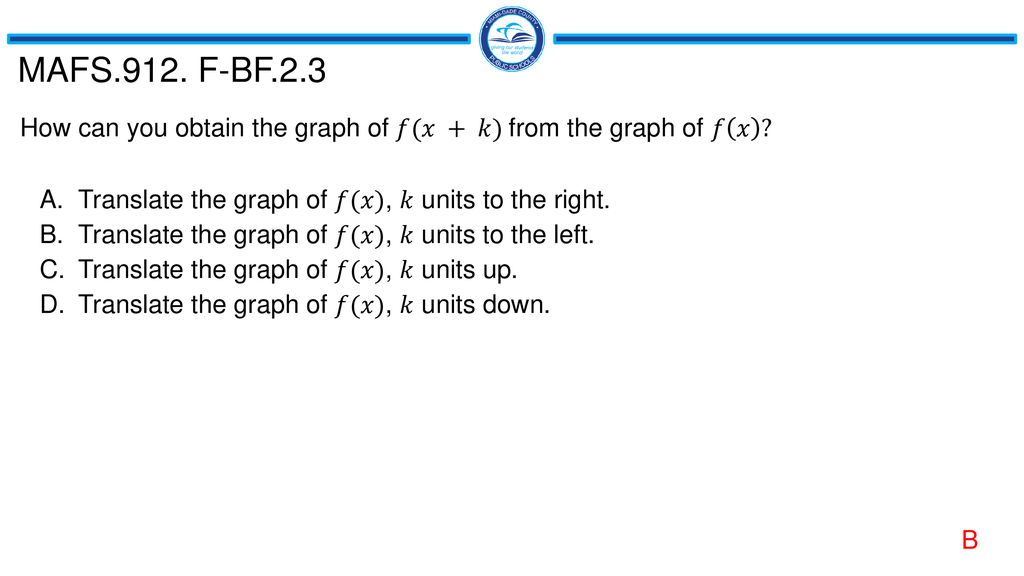
F x b x graph-In the chart below, just as in the previous chart, d>0, c>1, and (a,b)is a point in the graph of f(x) New How points in graph of f(x) visual e↵ect function become points of new graph f(xd) (a,b) 7!(ad,b) shift left by d f(xd) (a,b) 7!(ad,b) shift right by d f(cx) (a,b) 7!(1 ca,b) shrink horizontally by 1 c f(1 cx) (a,b) 7!(ca,b) stretchQuestion & answer choices in the image 1 If f (x) = k (x 2)*, where k is positive, what is the effect on the graph of f (x) as k increases?



Richard Hammack S Calculus I Lecture 42 The Definite Integral Youtube
Y = a√ (xh) k Square Root Graphing Radical Equations *Since positive AND negative numbers can be cube rooted, graph has 2 bends Graphing Radical Equations Example y = a∛ (xh) k (h, k) = (0, 0) a = 1 right 1 & up 1 a = 1 left 1 & down 1F b x g 10 5 4 1 0 8 f x 1 g fx 3 fx fb xg 2 3f b x g If is a function and k is a constant, then the graph of y k f x is the graph of y f x Vertical ly stretched by a factor of k, if k 1 Vertically compressed by a factor of k, if 01 kC x intercepts of the graph of a quadratic function The x intercepts of the graph of a quadratic function f given by f(x) = a x 2 b x c are the real solutions, if they exist, of the quadratic equation a x 2 b x c = 0 The above equation has two real solutions and therefore the graph has x intercepts when the discriminant D = b 2 4 a c is positive
Let's start with an easy transformation y equals a times f of x plus k Here's an example y equals negative one half times the absolute value of x plus 3 Now first, you and I ide identify what parent graph is being transformed and here it's the function f of x equals the absolute value of x And so it helps to remember what the shape of thatAnswer to The transformation of a function f(x) into function g(x) is given by g(x) = Af(Bx H) K Where the constants A vertically scales theExponential functions of the form f(x) = b x appear in different contexts, including finance and radioactive decay The base b must be a positive number and cannot be 1 The graphs of these functions are curves that increase (from left to right) if b > 1, showing exponential growth, and decrease if 0 < b < 1, showing exponential decay
This video shows how to use horizontal and vertical shifts together to graph a radical functionExploration of Sine Curves by Chad Crumley This exploration is of the function y = a sin b(x h) k, where a, b, h, and k are different values In particular, how do these values transform the graph of y= sin xBefore we begin, here is what that graphs look like with a, b equal to 1 and h, kGraph f (x)=2x f (x) = 2x f ( x) = 2 x Rewrite the function as an equation y = 2x y = 2 x Use the slopeintercept form to find the slope and yintercept Tap for more steps The slopeintercept form is y = m x b y = m x b, where m m is the slope and b b is the yintercept y = m x b y = m x b Find the values of m m and b b using



Plos One The X Gene Of Adeno Associated Virus 2 v2 Is Involved In Viral Dna Replication




Color Online Dirac Points Symbols Projected On The K X K Z Plane Download Scientific Diagram
Intuitively, a function is a process that associates each element of a set X, to a single element of a set Y Formally, a function f from a set X to a set Y is defined by a set G of ordered pairs (x, y) with x ∈ X, y ∈ Y, such that every element of X is the first component of exactly one ordered pair in G In other words, for every x in X, there is exactly one element y such that theIn this graph, f (x) has been moved over three units to the left f (x 3) = (x 3) 2 is f (x) shifted three units to the left This is always true To shift a function left, add inside the function's argument f (x b) gives f (x) shifted b units to the left Shifting to the right works the same way;Identify the effect on the graph of replacing f(x) by f(x) k, k f(x), f(kx), and f(x k) for specific values of k (both positive and negative);



What S New In Observable Plot 0 2 A Quick Tour Mbostock Cocotbodol



Yuu Must Showmum Tuu 1 Given F X 3 2x Plot A Chegg Com
The general form of the absolute value function is f (x) = axhk When "a" is negative, the Vshape graph opens downward and the vertex is the maximum When "a" is positive, the Vshape graph opens upward and the vertex is a minimum Hope this helps The variable b in both of the following graph types affects the period (or wavelength) of the graph y = a sin bx;Since f(−x) = e− (− x) 2 2 = e− 2 = f(x) and lim x→±∞ e− (−x)2 2 = 0, the graph is symmetry wrt the yaxis, and the xaxis is a horizontal asymptote • Wehave f0(x) = e−x 2 2 (−x) = −xe− x2 2 • Thus f ↑ on (−∞,0) and ↓ on (0,∞) • Atx = 0, f 0(x) = 0 Thus f(0) = e = 1 is the (only) local and



2




Graphing A Basic Function Youtube
Here's the graph of f x ( ) =tan( x)over this interval, with pertinent points marked To graph f x ( ) =Atan( Bx −C) D ;A The graph of f (x) is shifted up B The graph of f (x) is shifted down C Thế graph of F (x) is stretched vertically D The graph of f (x The graph of `y=sin (2x)` for `0 ≤ x ≤ 65` Now let's consider the phase shift Using the formula above, we will need to shift our curve by Phase shift `=c/b=1/2=05` This means we have to shift the curve to the left (because the phase shift is negative) by `05` Here is the answer (in green)



2




Is The Following 68 The Graph Of A Real Valued Function F X Is The Fa
• The period is B π • Find two consecutive asymptotes by solving 2 Bx C π − = and 2 Bx C π − =− • Find an xintercept by taking the average of the consecutive asymptotesThe graph of the logarithmic function y = log x is shown (Remember that when no base is shown, the base is understood to be 10) Observe that the logarithmic function f (x) = log b x is the inverse of the exponential function g (x) = b x It has the following properties The domain is the set of all positive real numbers 1 f (x) = log b x is not defined for negative values of x, or for 0 2 The14 Transforming f(x) = x into g 3(x) = 2x−3 The graph of y= g 3(x) is in Figure 14 It is obtained by the following transformations (a) B= 2 Compress horizontally by a factor of 1 2 (b) k= −3 Shift 3 units down Figure 14 2 4 6 46 6 4 2 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 x y Original Function Transformation 15 Transforming f(x) = √ xinto g 4(x) = √ −x4



2




A Hybrid Gradient Method For Strictly Convex Quadratic Programming Oviedo Numerical Linear Algebra With Applications Wiley Online Library
F(x)=96kx x2 k x≠0 f′(x) −192k x3 −192 x−3 k 1b The graph of has a local minimum point at 2 marks Show that Markscheme at local minimum (M1) Note Award (M1) for seeing (may be implicit in their working) (A1) (AG) Note Award (A1) for substituting in their , provided it leads to The conclusion must be seen for the (A1)Graphing Logarithmic Functions The function y = log b x is the inverse function of the exponential function y = b x Consider the function y = 3 x It can be graphed as The graph of inverse function of any function is the reflection of the graph of the function about the line y = x So, the graph of the logarithmic function y = log 3 ( xThe graph of f (x) 1 f(x) 1 f (x) 1 is the graph of f (x) f(x) f (x) shifted up by 1 1 1 unit Thus, to move a function up or down, we add to the outside of the function f (x) d f(x) d f (x) d is the graph of f (x) f(x) f (x) shifted up by d d d units Horizontal Translation To move a graph right horizontally by 1 unit, we adjust




11 1 Chebyshev Points Of The First Kind Hackmd



Www Mickmacve Com Uploads 2 9 5 2 19 01 22 Modulus Graphs Pdf
Plugging these values into the general form f(x) = a f b(x − h) k where f(x) = , we get f(x) = 4 3 This can be simplified to f(x) = 3 _____ The mapping rule is useful when graphing functions with transformations Any point (x, y) of a parent function becomes (How to graph a quadratic function using transformations Given f(x) and g(x) = f(x) k, use the graph to determine the value of k Graph of two lines f of x equals 1 over 3 x plus 2 and g of x equals 1 over 3 x plus 5 A) 2 B) 3 C) 4 D) 5 Categories Uncategorized Leave a Reply Cancel reply Your email address will not be published Required fields are marked *



Rodrigopacios Github Io Mrpacios Download Definiteintegralsms Pdf



Graph Exponential Functions Using Transformations College Algebra
2 Exponential Growth Function f(x) = a·bxh k , b>1 "a" stretches the or shrinks the graph by moving the yint to (0,a) and the second point to (1,ab) Recall in the parent graph a=1, so the yint is (0,1) and the second point is just (1,b) "h" shifts the graph horizontally Remember to watch the sign on "h", the formula must read subtract h before you can find theSine Graph Calculator Enter in the values for f(x) = Asin(B(xh))k into the sine graph calculator to check your answer Try the free Mathway calculator and problem solver below to practice various math topics Try the given examples, or type in your own problem and check your answer with the stepbystep explanationsF (x – b) is f (x) shifted b units to




Richard Hammack S Calculus I Lecture 42 The Definite Integral Youtube




A Modulus And B Phase Of The Amplitude Transfer Function Q F X As Download Scientific Diagram
A cubic polynomial function f is defined by f (x) = 4x^3 ax^2 bx k where a, b and k are constants The function f has a local minimum at x = 1, and the graph of f has a point of inflection at x= 2 a) Find the values of Calculus (Continuity and Differentiability)The graph of y=Af(x) can be obtained from the graph of y=f(x) by multiplying each ordinate value of the latter by A and graphing the points with these new ordinate values Values where A>1 result in a vertical _____ of the graph of y=f(x) Values where 0The graph of f (x) is shown (see figure) 7x f (x) = (x² 4 Nordrowa (a) Find the following limits L = lim f (x) = K= lim f (x) = (b) Determine Xand x2 in terms of € X1 = X2 (c) Determine M, where M > 0, such that F (x) L < for x > M ME (d) Determine N, where N < 0, such that f (x) Kl



2



Sensors Free Full Text Through Wall Uwb Radar Based On Sparse Deconvolution With Arctangent Regularization For Locating Human Subjects Html
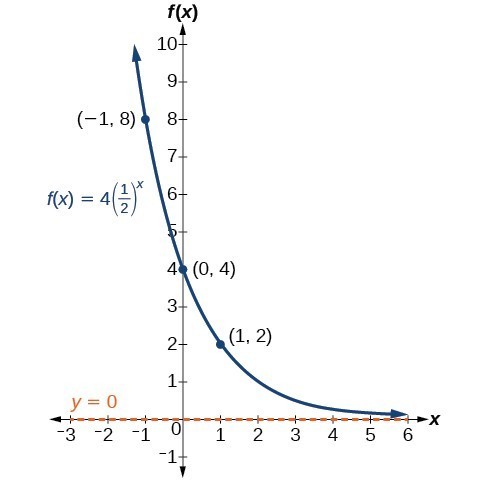
Y = a cos bx;The point (1,b) ( 1, b) is on the graph This is true of the graph of all exponential functions of the form y =bx y = b x for x > 1 x > 1 Graph of y=2x y = 2 x The graph of this function crosses the y y axis at (0,1) ( 0 , 1) and increases as x x approaches infinity The x x axis is a horizontal asymptote of the functionSince b < 1, the graph will be decreasing towards zero Since a > 0, the graph will be concave up We can also see from the graph the long run behavior as x → ∞ , f(x) → 0, and as x → –∞, f(x) → ∞ To get a better feeling for the effect of a and b on the graph, examine the sets of graphs below The first set shows various




4 Numerical Methods Root Finding Secant Method Modified
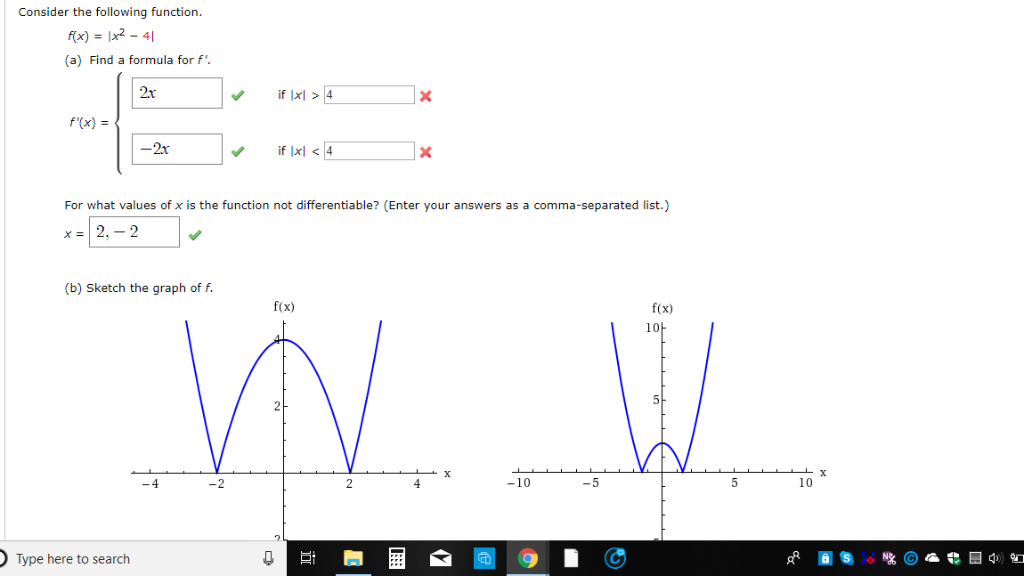



Consider The Following Function F X X2 41 A Chegg Com
Also note that the graph shoots upward rapidly as x increases This is because of the doubling behavior of the exponential Exponential Decay In the form y = ab x, if b is a number between 0 and 1, the function represents exponential decay The basic shape of an exponential decay function is shown below in the example of f(x) = 2 −xMost exponential functions are defined as (refer to the graphs to see how each factor shifts from the general form) f (x)=ab xh k In this case, here are the values of a, b, h, and k a=2 b=15 h=0 k=2 Thus, this are the effects of a, b, h, and k a determines the height of the key point, or the y intercept where h = 0, above theFor example, when B=2, the graph has a period of pi and is a reflection across the yaxis of y=sin(2x) When B=0, the graph degenerates to a line on the xaxis The period of the graph is (2pi)/B For B>0, as B increases, the period of the graph decreases For B



4 2 Algebra 2 Study Site




Given F X And G X F K X Use The Graph To Determine The Value Of K A 3 B 1 3 C 1 3 D Brainly Com
Find the value of k given the graphsRelated Pages Graphs Of Functions Parent Functions And Their Graphs Transformations Of Graphs More PreCalculus Lessons Common Core (Functions) We shall learn how to identify the effect on the graph of replacing f(x) by f(x) k, kf(x), f(kx), and f(x k) for specific values of k (both positive and negative);Let 23 4R be the region enclosed by the graph of fx x x ( ) =− 43 and the horizontal line y =4, as shown in the figure above (a) Find the volume of the solid generated when R is rotated about the f x dx f x dx Sample 2A Score 9 The student earned all 9 points Sample 2B
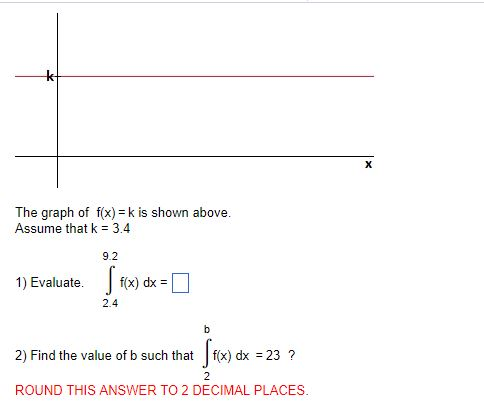



The Graph Of F X K Is Shown Above Assume That K 3 4 Chegg Com



2
444 Chapter 8 Graphing Quadratic Functions Graphing y = a(x − h)2 k Graph g(x) = −2(x 2)2 3 Compare the graph to the graph of f (x) = x2 SOLUTION Step 1 Graph the axis of symmetry Because h = −2, graph x =2 −2 Step 2 Plot the vertex Because h = −2 and k = 3, plot (−2, 3) Step 3 Find and plot two more points on the graph Choose two xvalues less than the xcoordinateFor the base function f (x) and a constant k > 0, the function given by g(x) = k f (x), can be sketched by vertically stretching f (x) by a factor of k if k > 1 or by vertically shrinking f (x) by a factor of k if 0 < k < 1 Horizontal Stretches and Shrinks For the base function f (x) and a constant k, where k > 0 and k ≠ 1, theTransformations of Graphs (a, h, k) Consider the function y = f (x) We're going to refer to this function as the PARENT FUNCTION The following applet allows you to select one of 4 parent functions The basic quadratic function f (x) = x^2 The basic cubic function f (x) = x^3 The basic absolute value function f (x) = x The basic square



2




Sketch The Graph Of The Quadratic Expression Y F X 2 X 2 B X C 4 1 B 2 C 3 C A 0 B 0 B 2 4 A C 0 B A 4 B 6 C 2 D A C B 2 D 0
The graph always lies above the xaxis, but becomes arbitrarily close to it for large negative x;Transformations of a Polynomial Function You need to recall the general equation for transformations which is y = a f (k (xd) ) c Where if a is a > 1 It is a vertical stretch 0 < a < 1 It is a vertical compression a < 0 There is a reflection in the x axis Where if k isFind the value of k given the graphs Experiment with cases and illustrate an explanation of the effects on the graph using technology
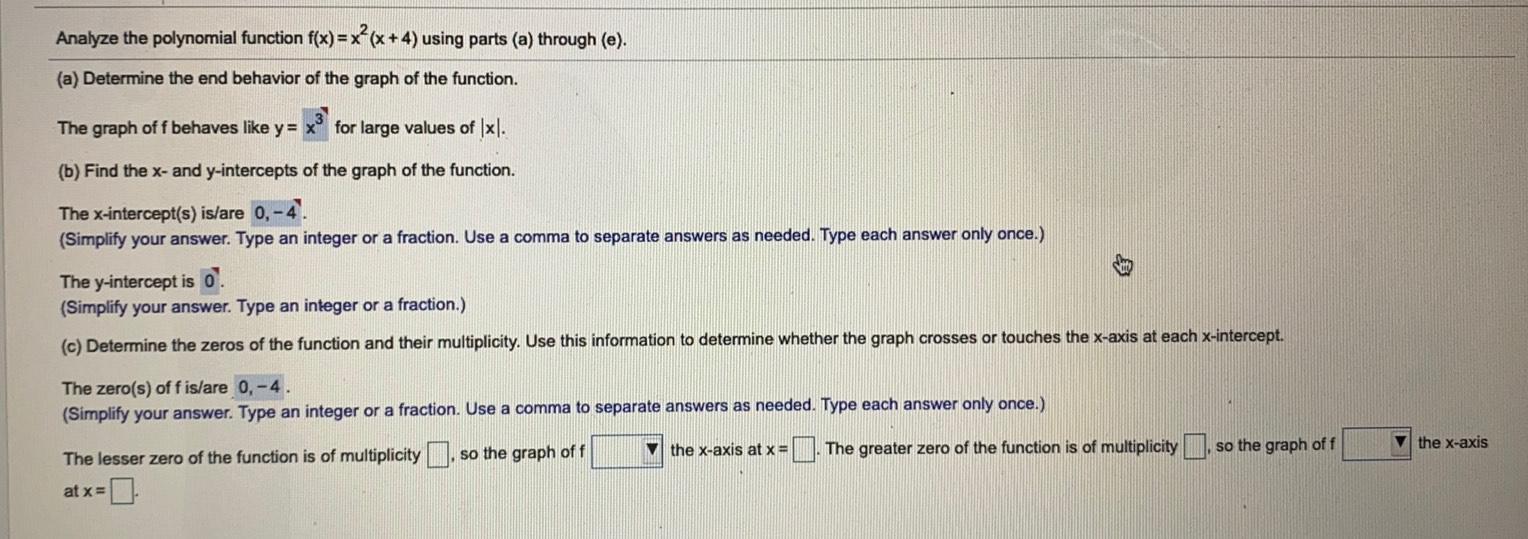



Analyze The Polynomial Function F X X X 4 Using Pa Math
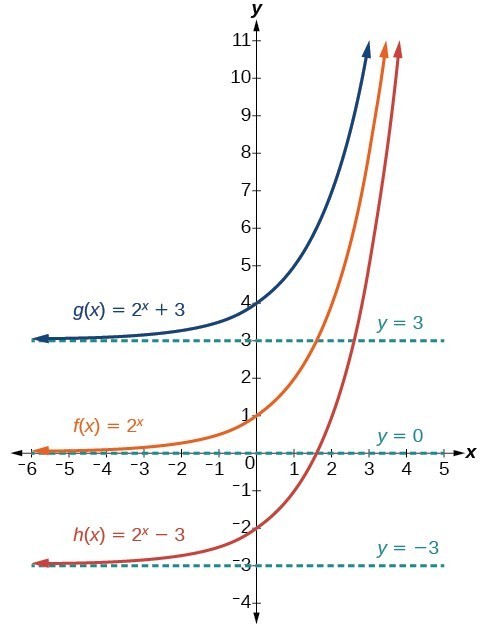



Graph Exponential Functions Using Transformations College Algebra
Graph f (x)=x Find the absolute value vertex In this case, the vertex for is Tap for more steps To find the coordinate of the vertex, set the inside of the absolute value equal to In this case, Replace the variable with in the expression The absolute value is the distance between a number and zero The distance between and isF(x)=96kx x2 k x≠0 f′(x) −192k x3 −192 x−3 k 6b The graph of has a local minimum point at 2 marks Show that Markscheme at local minimum (M1) Note Award (M1) for seeing (may be implicit in their working) (A1) (AG) Note Award (A1) for substituting in their , provided it leads to The conclusion must be seen for the (A1) toAdding or subtracting a constant \(k\) to a function has the effect of shifting the graph up or down vertically by \(k\) units Graph of y = f(x) This has the effect of reflecting the graph about




16 Diagram Shows The Graph Of See How To Solve It At Qanda
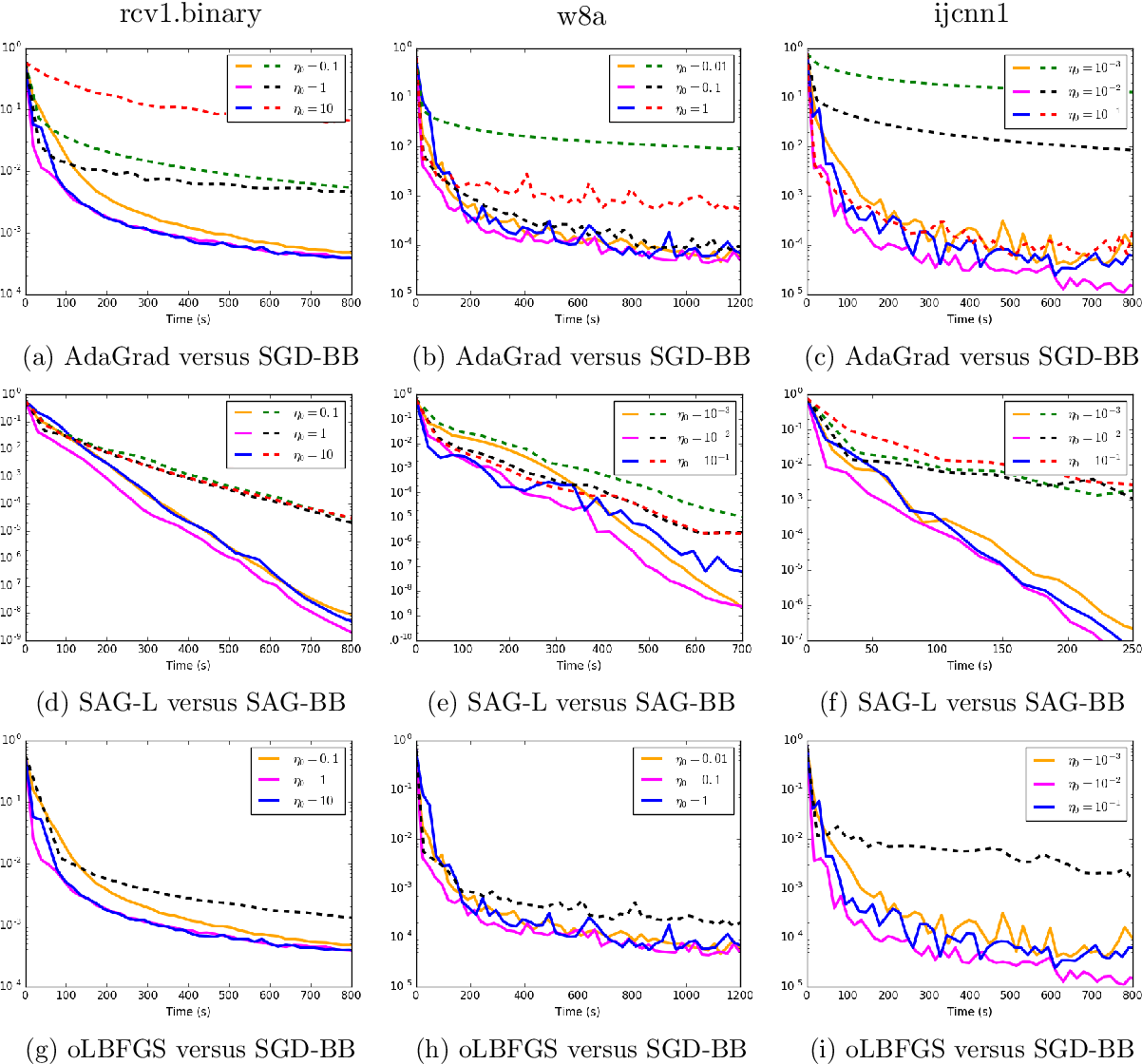



Figure 3 From Barzilai Borwein Step Size For Stochastic Gradient Descent Semantic Scholar



2



Zoom Grapher Geogebra
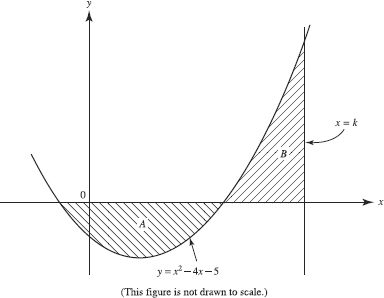



Ap Calculus Ab Question 347 Answer And Explanation Crackap Com




Focal Sib Xl Stand Pied Sib Xl Using Pdf Download Manualslib




A Modulus And B Phase Of The Phase Transfer Function P F X As A Download Scientific Diagram
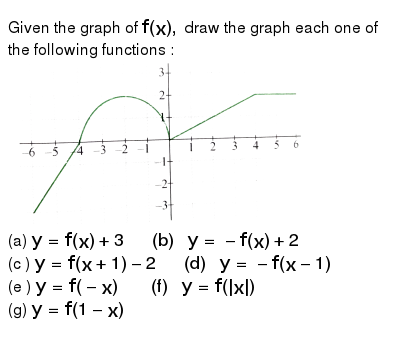



If The Graph Of Y F X Is Transformed Into The Graph Of 2y 6



Challenge To Better Agreement Between Theoretical Computations And Measurements In Ship Hydrodynamics Ships Water Waves Method 1 Method 2 Method 3 0 Experiment Shintani X L Figure 12 Added Resistance Coefficient



Algebraic Transformations Geogebra
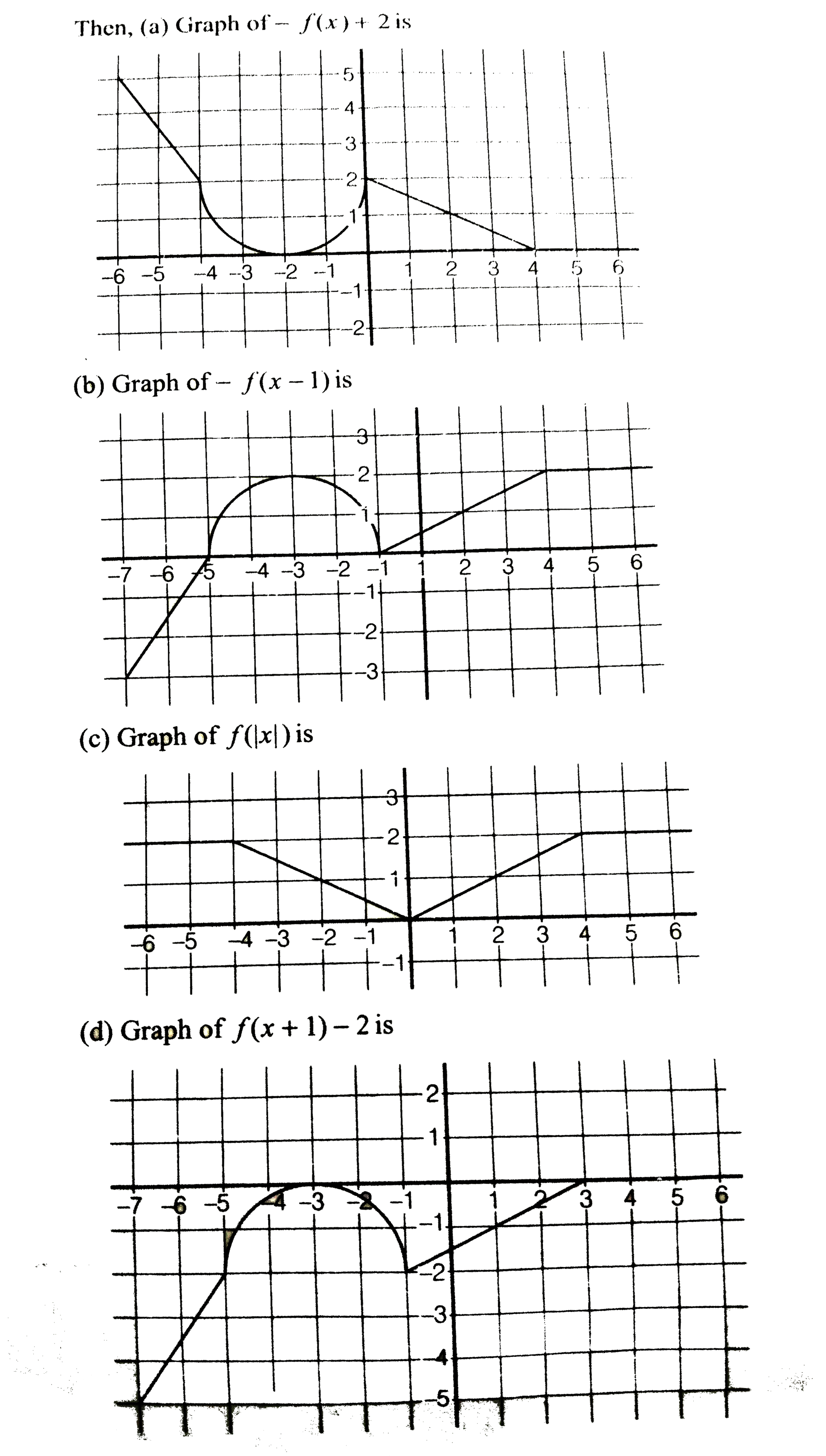



Which Statement Is True About F X 2 1 6 X 3 A The Graph Of F



2




Accuracy Improvement Of Echographic Speckle Tracking Based On Analysis Of Estimation Error Caused By Acoustic Pressure Field
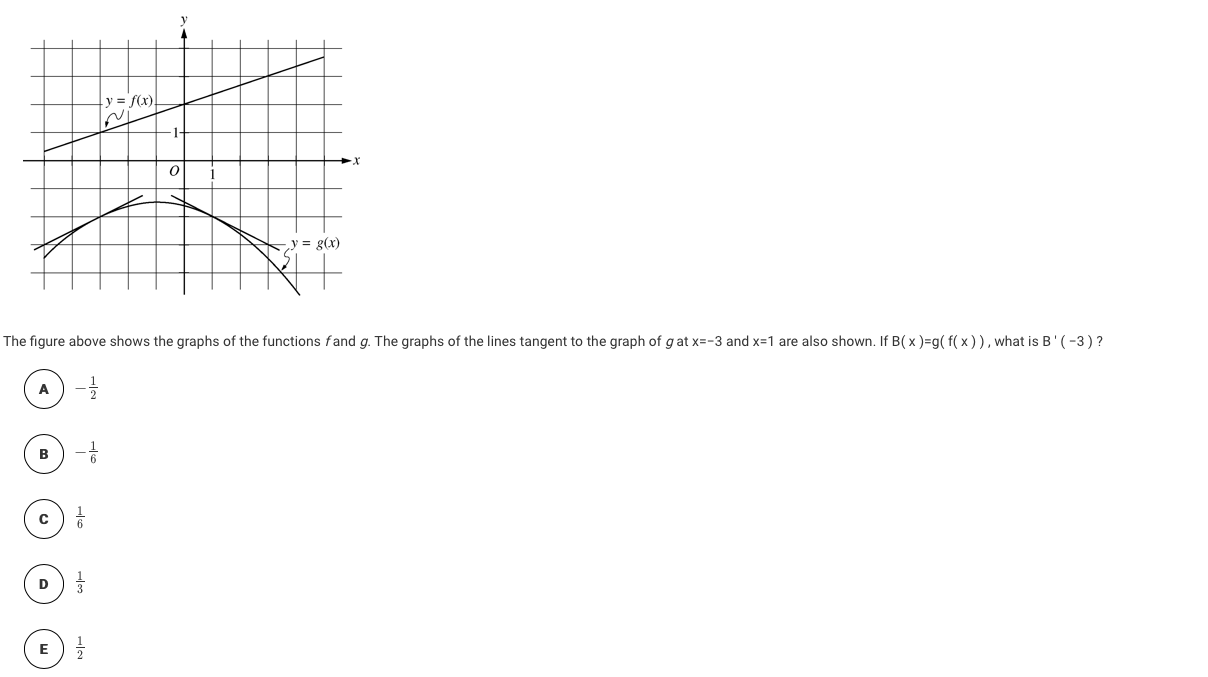



Y F Xl Y G X The Figure Above Shows The Graphs Chegg Com
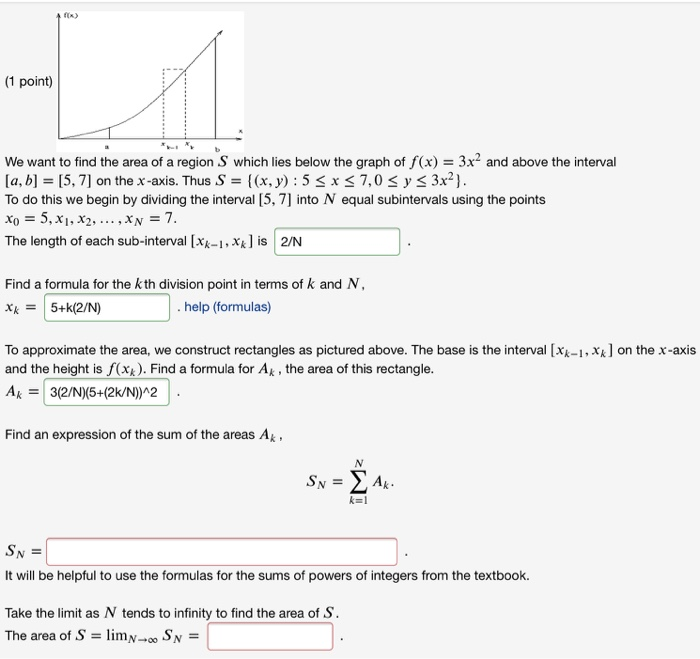



1 Point We Want To Find The Area Of A Region S Chegg Com




Scaled Error S K 1 2 F X K F X Of The Generalized Nag C Download Scientific Diagram



Solved The Graph Of F G X Is Shown Below Which Of The Options Below Could Be F X And G X Course Hero
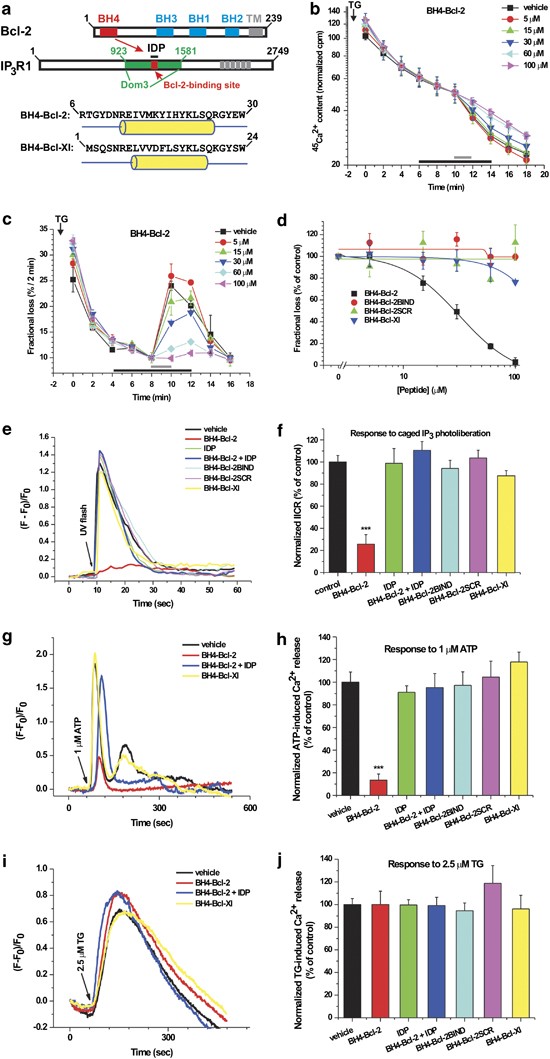



Selective Regulation Of Ip3 Receptor Mediated Ca2 Signaling And Apoptosis By The Bh4 Domain Of l 2 Versus l Xl Cell Death Differentiation



Http Www Math Ncu Edu Tw Cchsiao Ocw Calculus Note Ch7 Pdf



2



Www Math Utah Edu Wortman 1050 Text If Pdf



Q Tbn And9gcqgxordtnbyapfjd3lmlujrvslb5x3ac Hjy Sjwpnftor78qyt Usqp Cau
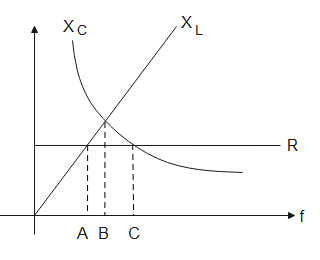



Figure Shows Variation Of R Xl And Xc With Frequency Class 12 Physics Cbse



Www M3 Ma Tum De Foswiki Pub M3 Numerikp09 Uebungsaufgaben Numueb06 Loe Pdf



Http Cs Uok Edu In Files f07 9550 4aeb 6f 5d802d56b46d Custom Tutorial5 Pdf




Exponential Functions A Simple Guide To Exponential Logarithmic And Inverse Functions
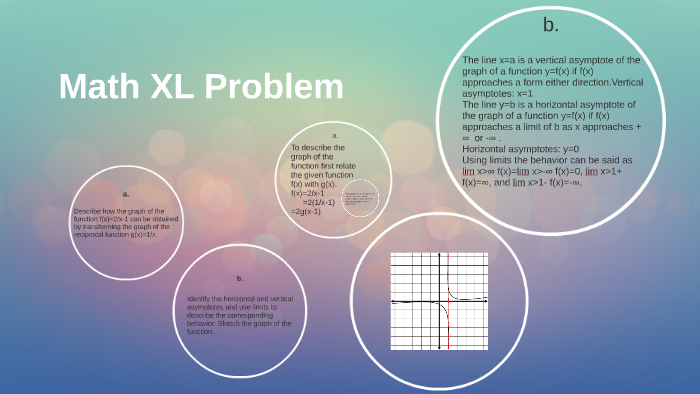



Math Xl Problem By Brittany Ketchum On Prezi Next



Search Q Exponential Function Tbm Isch



Www Uni Muenster De Amm Num Vorlesungen Numerik1 Ws06 Aufgaben06 Blatt8 Pdf



Secure Media Collegeboard Org Digitalservices Pdf Ap Apcentral Ap13 Calculus Ab Q4 Pdf




Wiki Konstanten Faktor Potenzregel Fit In Mathe Online




Log 10 F X K With Initial Guess X 0 1 0 28 T For Example 1 Download Scientific Diagram



2




The Diagram Below Shows Part Of The Graph Of The Quadratic Function F X A X H X K With The Brainly Com



Applied Thermodynamics For Engineers Qual To T L L R Then 1 2 4 3 3 4 Being Drawnhorizontally And 1 3 Vertically Is Equal To R X L R 12 X 2




Parabola Through Three Points With Tikz Tex Latex Stack Exchange
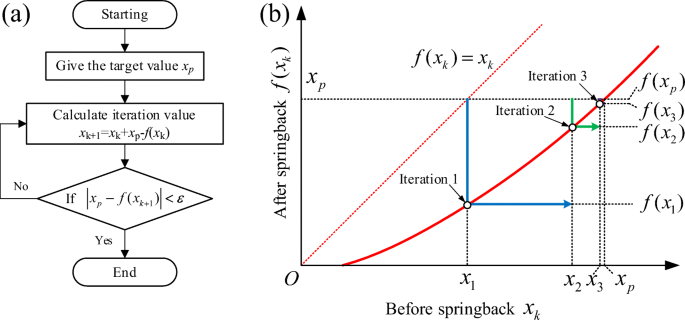



Research On Iterative Compensation Method For Springback Control Based On Implicit Equation Springerlink



1
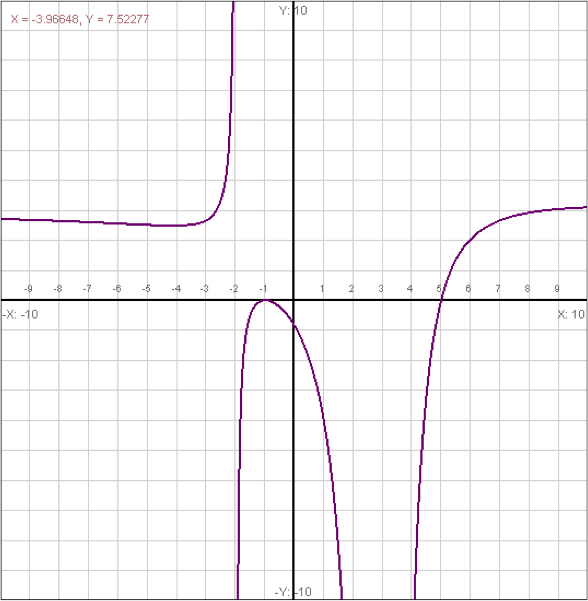



Journal Entry 3 The Graph Of Chegg Com
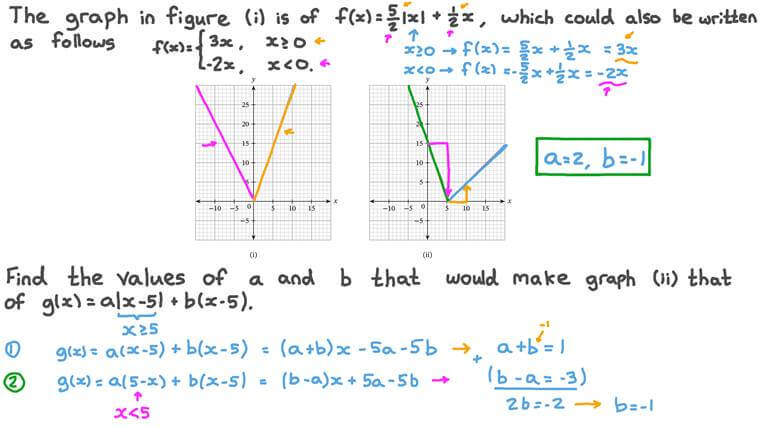



Lesson Absolute Value Functions Nagwa
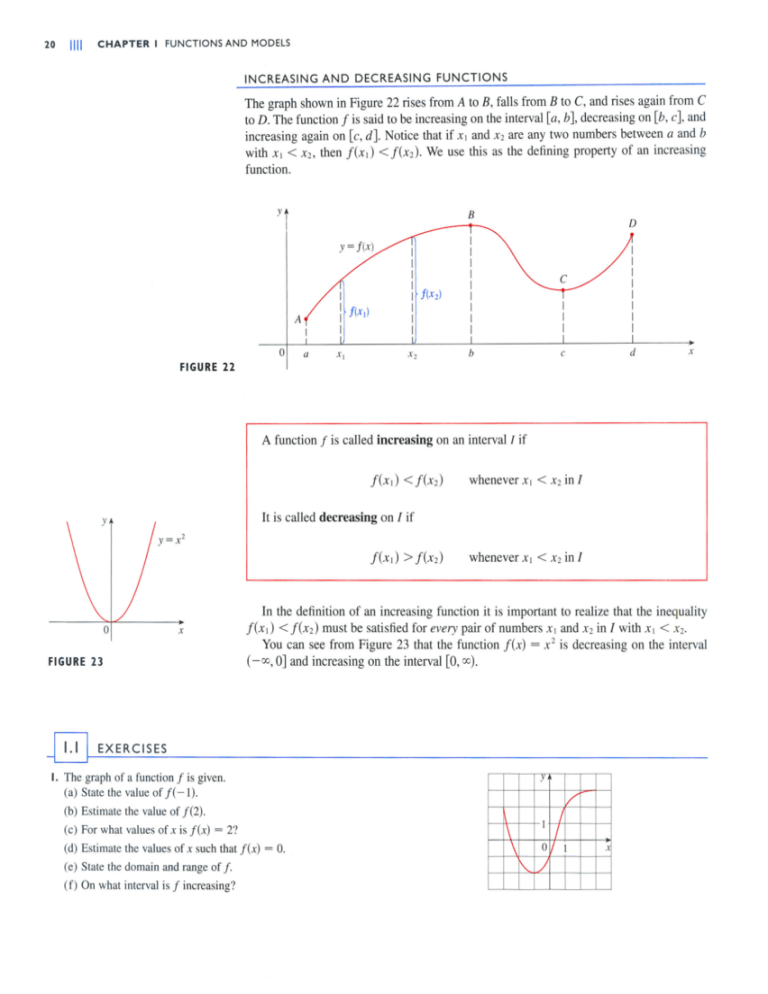



Chapter 1
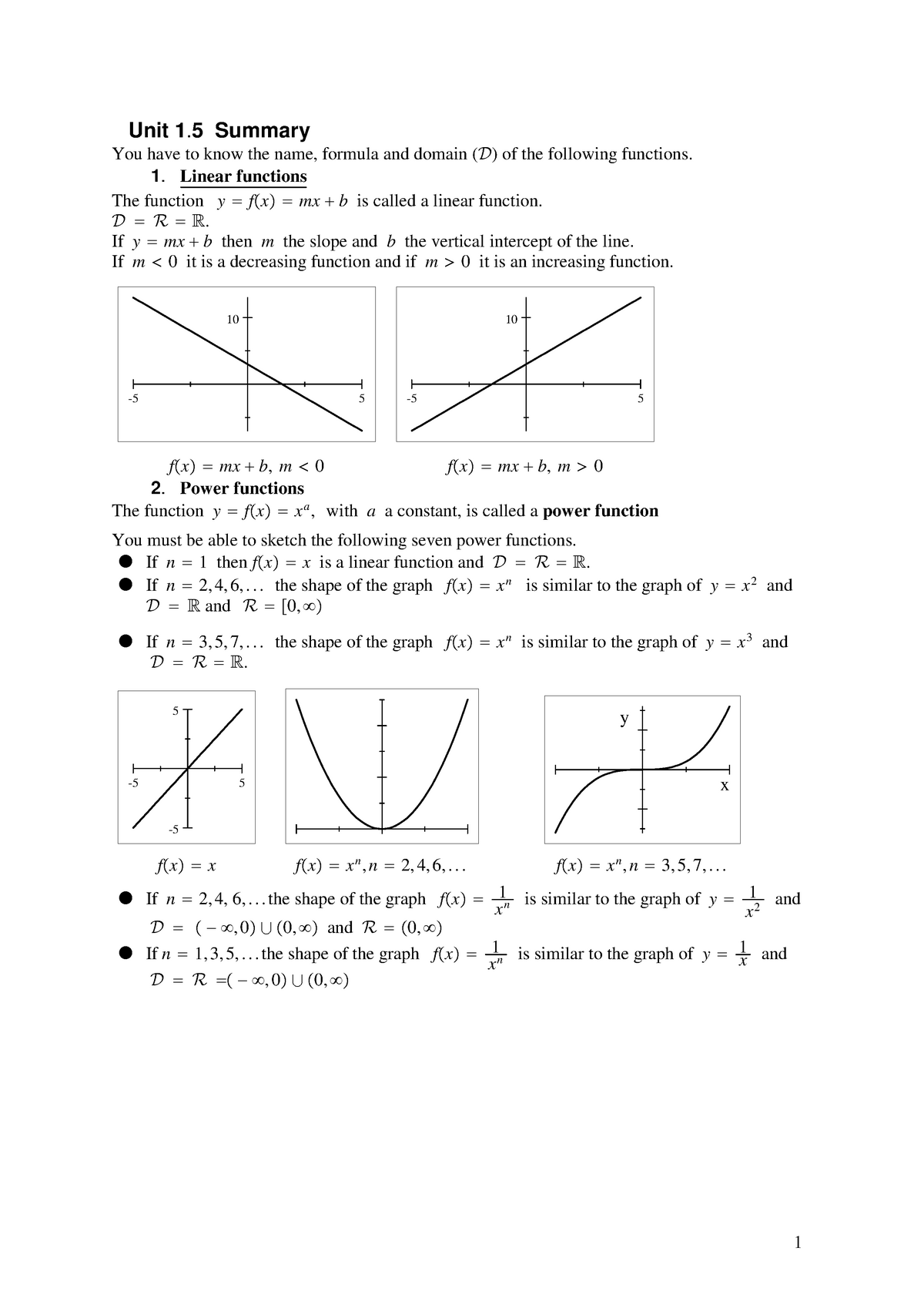



Unit 1 5 Summary Studocu
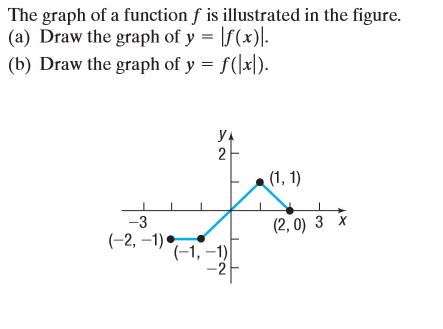



Answered The Graph Of A Function F Is Bartleby



Sensors Free Full Text Through Wall Uwb Radar Based On Sparse Deconvolution With Arctangent Regularization For Locating Human Subjects Html




How To Get Color Of Most Recent Plotted Line In Python S Plt Stack Overflow
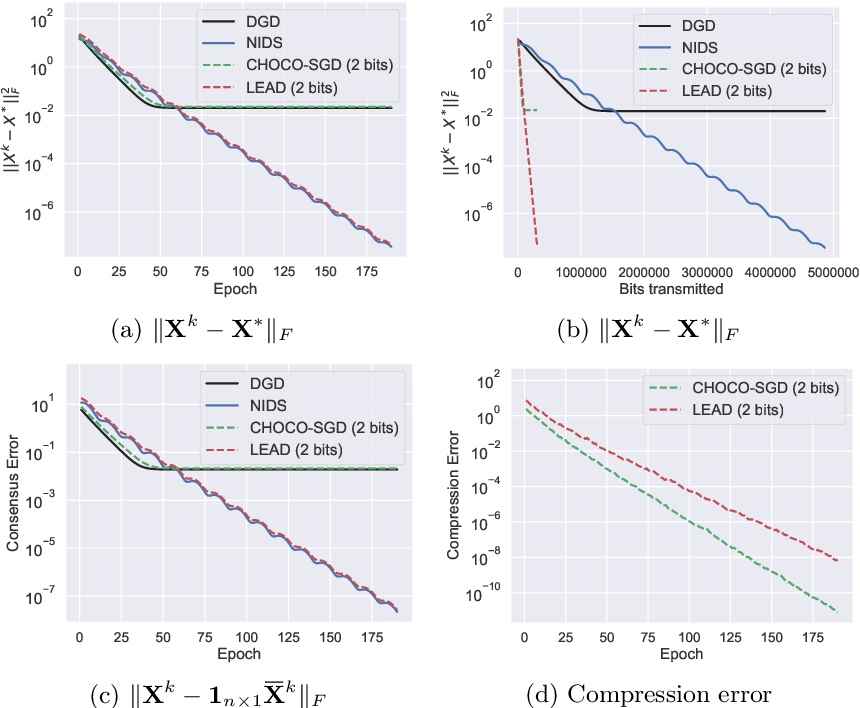



Linear Convergent Decentralized Optimization With Compression Paper And Code Catalyzex



Exploration Of Polar Graphs Cosine Geogebra
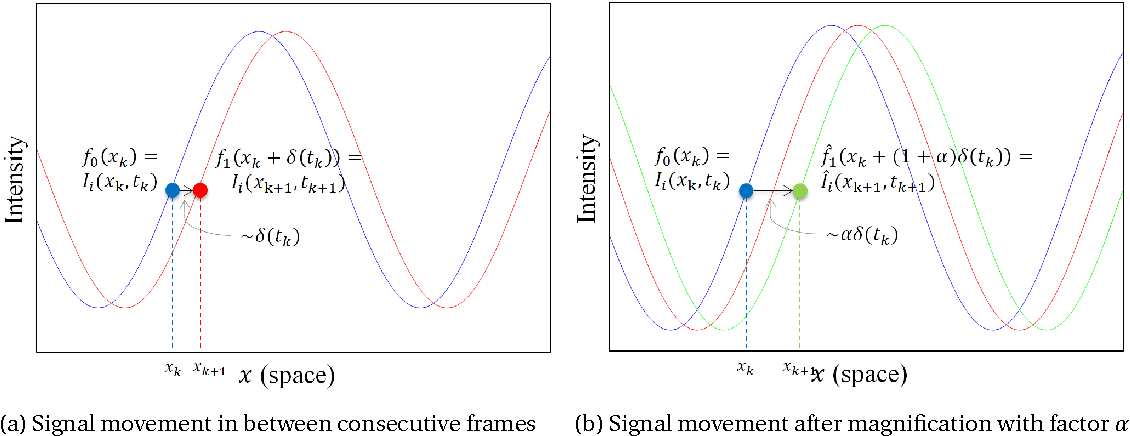



Eulerian Video Acceleration Magnification Semantic Scholar




Graph The Equations In Your Notes Use The




Welcome September 28 Homework Quiz 3 2 Homework Questions Ppt Download
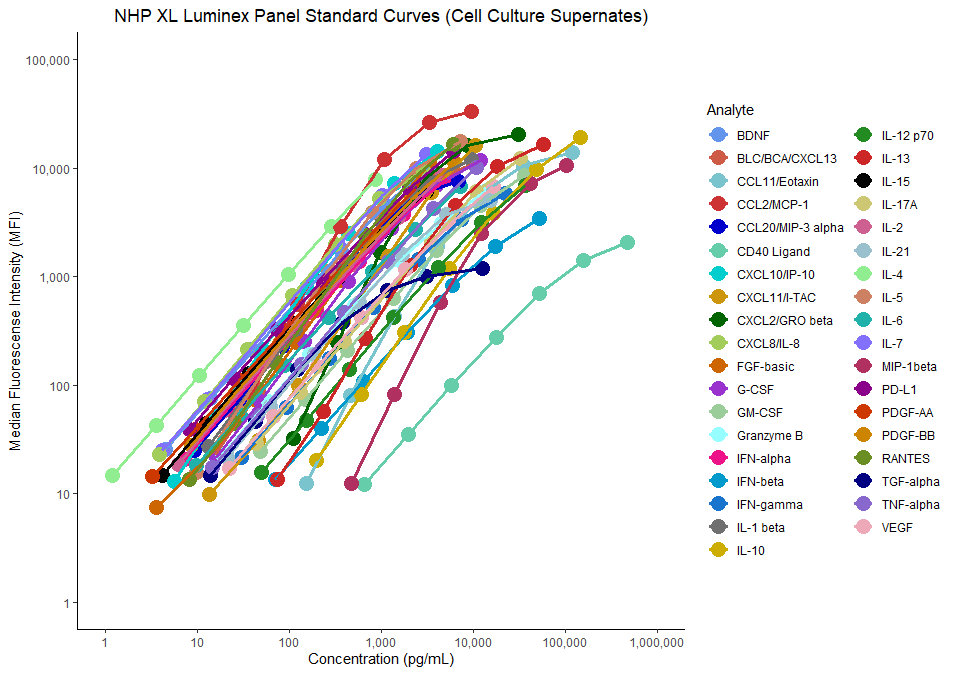



Nhp Xl Cytokine Luminex Performance Premixed Kit Fcstm21 R D Systems



2



2




The Diagram Below Shows The Graph Of Fx 1 X 3 1 Gauthmath



5 1 Area And Estimating With Finite Sums
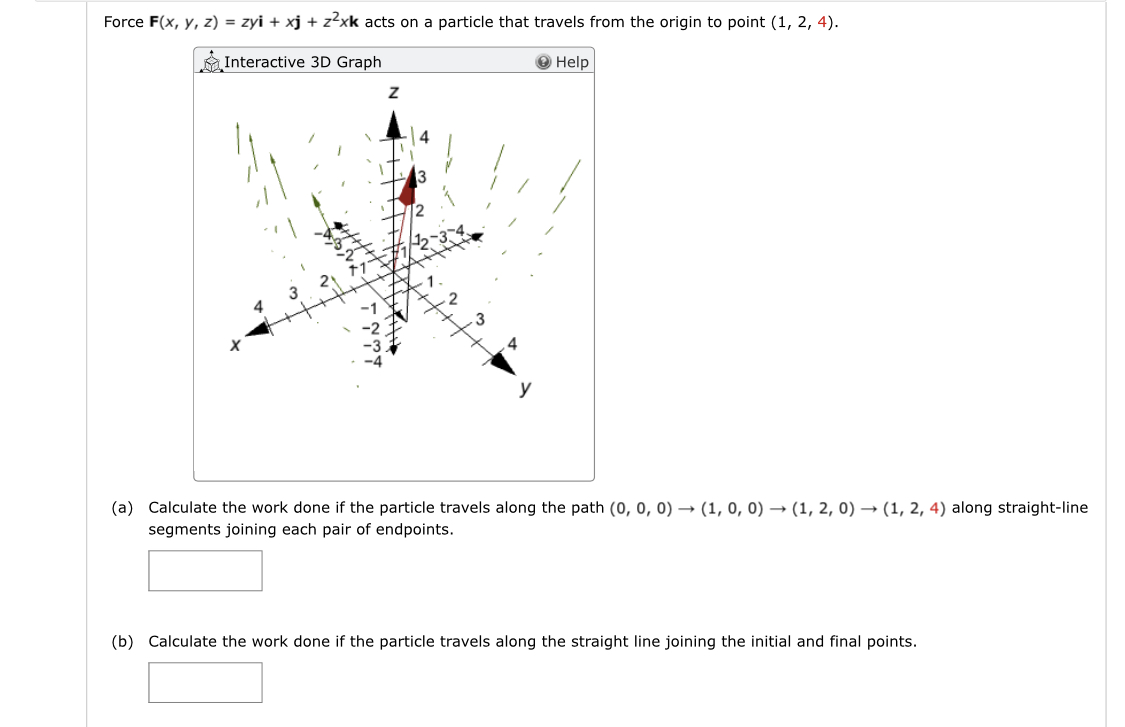



Answered Force F X Y Z Zyi Xj Z Xk Acts Bartleby




Can Someone Please Explain This To Me October 18 Qas Sat
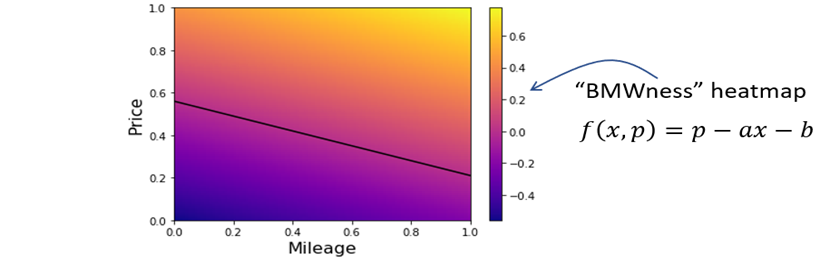



15 Classifying Data With Logistic Regression Math For Programmers 3d Graphics Machine Learning And Simulations With Python



2
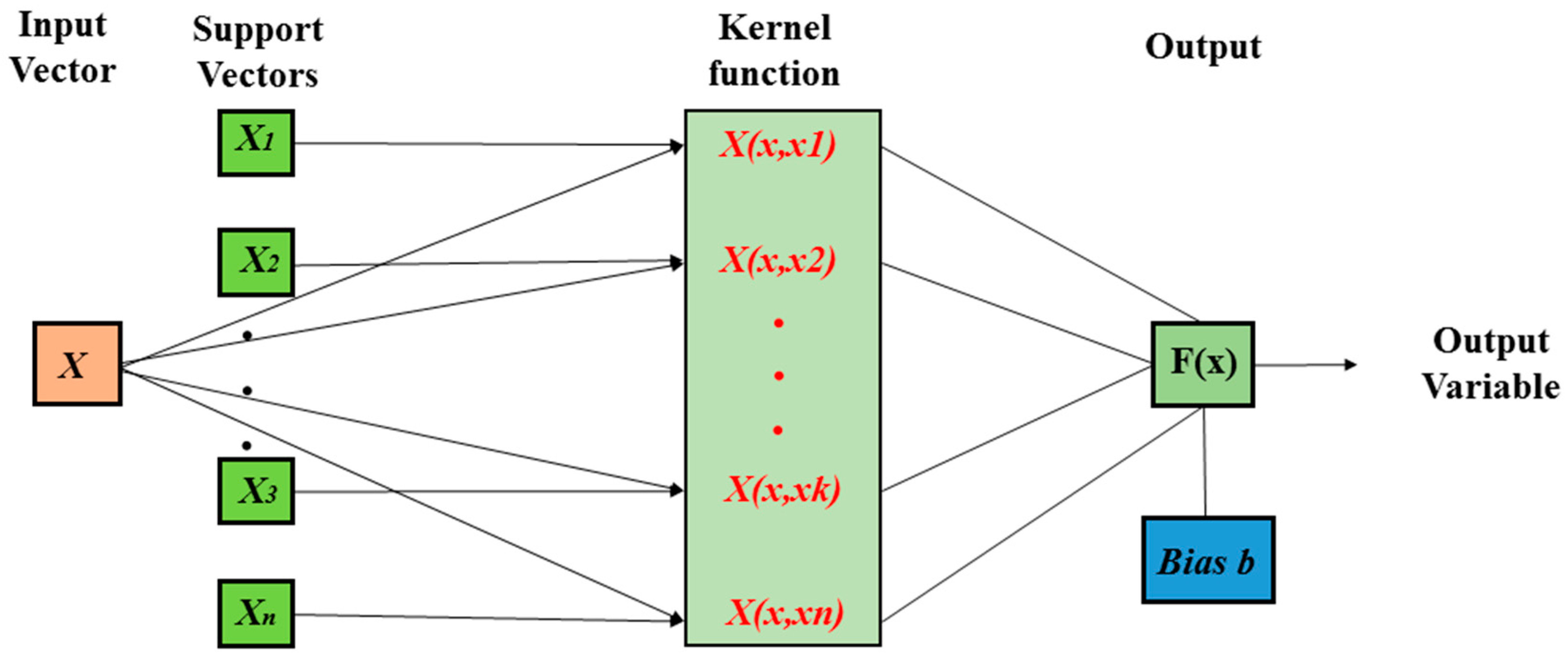



Water Free Full Text Simulation Of Titicaca Lake Water Level Fluctuations Using Hybrid Machine Learning Technique Integrated With Grey Wolf Optimizer Algorithm Html




A Comparison Of Linear Interpolation Models For Iterative Ct Reconstruction Hahn 16 Medical Physics Wiley Online Library



Functions And Modeling Ppt Download




The Graph Of A Constant Function F X K Is




Realistischer Mathetafelhintergrund Kostenlose Vektor



F X Kx B K 0 B 0 Plainness Opensea




6 5 Areas Of Surfaces Of Revolution And The Theorems Of Pappus Pdf Free Download




Mca645 Cu Mca Sem Ii Statistical Numerical Methods Converted Converted Flip Book Pages 51 100 Pubhtml5



Csumath155 Files Wordpress Com 17 12 Multiple Choice Pdf




Integrating Functions Of Several Variables




5 The Diagram Shhows The Graph Of Hx Figur Gauthmath
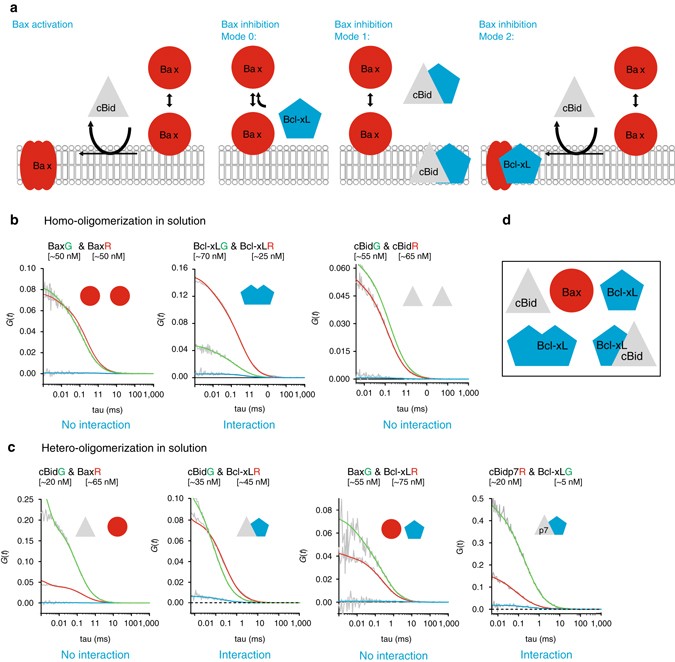



Quantitative Interactome Of A Membrane l 2 Network Identifies A Hierarchy Of Complexes For Apoptosis Regulation Nature Communications



Q Tbn And9gcsl0jyluxfxjjcizs7jyiyflsxbm6hpbpzdawckl4kjhmo0pmir Usqp Cau




A Short Note On The Existence Of Infinite Sequences Of G Graphs Of Graphs Sciencedirect
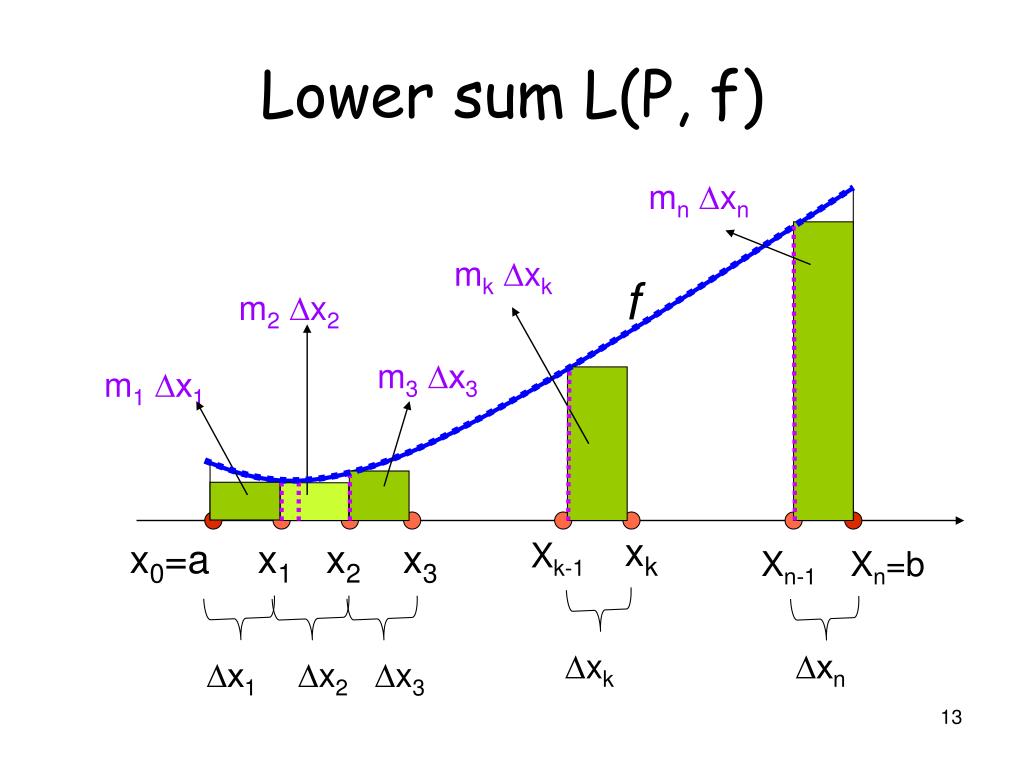



Ppt Proper Univariate And Multivariate Integrals Powerpoint Presentation Id



2




On The Opportunistic Topology Of Taxi Networks In Urban Mobility Environment



No comments:
Post a Comment